Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumor Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Prognosis
Frequently Asked Questions
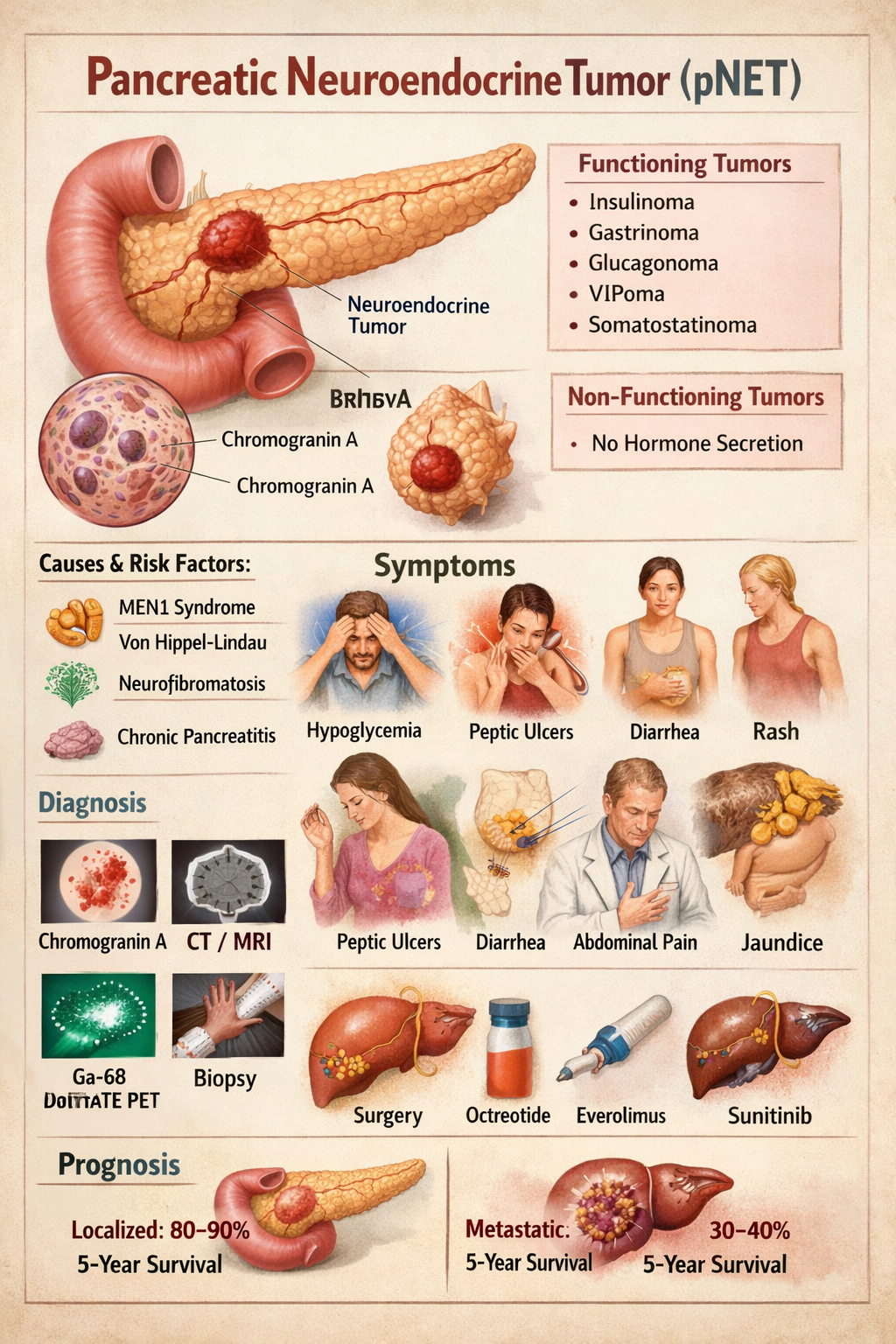
A pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor is a rare tumor arising from hormone producing islet cells of the pancreas that may be hormone secreting or non functioning
The main types include insulinoma, gastrinoma, glucagonoma, VIPoma, somatostatinoma and non functioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
Symptoms include fasting hypoglycemia, sweating, tremors, confusion, blurred vision and relief after taking glucose
Diagnosis is based on hormone blood tests, chromogranin A levels, imaging with CT or MRI, endoscopic ultrasound and Ga 68 DOTATATE PET scan
Chromogranin A is a tumor marker commonly elevated in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and is used for monitoring disease
Ga 68 DOTATATE PET CT is the most sensitive and specific imaging for detecting pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and metastases
Zollinger Ellison syndrome is caused by gastrin secreting pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors called gastrinomas
MEN1 is a genetic disorder causing multiple endocrine tumors including pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors along with pituitary and parathyroid tumors
Treatment includes surgical removal, somatostatin analogs, targeted therapy like everolimus or sunitinib, chemotherapy and radionuclide therapy
Localized pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors have good prognosis with high survival while metastatic disease has lower but still better survival compared to pancreatic cancer