Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
Mitral Regurgitation Detailed Management Guidelines Diagnosis and Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
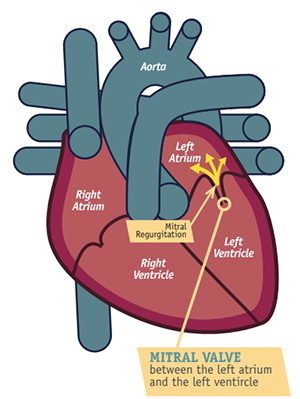
Mitral regurgitation is a valvular heart disease in which blood flows backward from the left ventricle into the left atrium during systole due to incomplete closure of the mitral valve.
Causes include mitral valve prolapse, rheumatic heart disease, infective endocarditis, papillary muscle rupture after myocardial infarction, dilated cardiomyopathy, and ischemic heart disease.
Acute mitral regurgitation develops suddenly and causes pulmonary edema and shock, while chronic mitral regurgitation develops gradually with compensatory left atrial and ventricular dilation.
Symptoms include exertional dyspnea, fatigue, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, palpitations due to atrial fibrillation, and hemoptysis in advanced disease.
Mitral regurgitation produces a holosystolic murmur best heard at the apex and radiating to the axilla, often accompanied by a soft first heart sound.
Echocardiography is the gold standard investigation, providing information about valve anatomy, severity of regurgitation, and left ventricular function.
Severe mitral regurgitation is defined by effective regurgitant orifice area ≥0.40 cm², regurgitant volume ≥60 mL, or vena contracta width ≥0.7 cm.
Indications include symptomatic severe mitral regurgitation, asymptomatic severe mitral regurgitation with left ventricular dysfunction, pulmonary hypertension, new-onset atrial fibrillation, or progressive ventricular dilation.
Mitral valve repair preserves left ventricular function, has lower operative mortality, avoids long-term anticoagulation, and provides better long-term survival.
Functional mitral regurgitation occurs due to left ventricular dilation and remodeling with structurally normal mitral valve leaflets, commonly seen in ischemic or dilated cardiomyopathy.
Medications provide symptomatic relief and delay progression but do not correct the valve lesion; they include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, and anticoagulants when indicated.
MitraClip is used in patients with severe symptomatic functional mitral regurgitation who remain symptomatic despite optimal medical therapy and are at high surgical risk.
Atrial fibrillation increases the risk of thromboembolism and worsens symptoms due to loss of atrial contribution to ventricular filling.
Chronic mitral regurgitation with preserved left ventricular function is usually well tolerated during pregnancy due to reduced systemic vascular resistance.
Left ventricular systolic dysfunction is the most important predictor of poor prognosis and mortality in chronic mitral regurgitation.