Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Postpartum Hemorrhage Causes Diagnosis and Management
Frequently Asked Questions
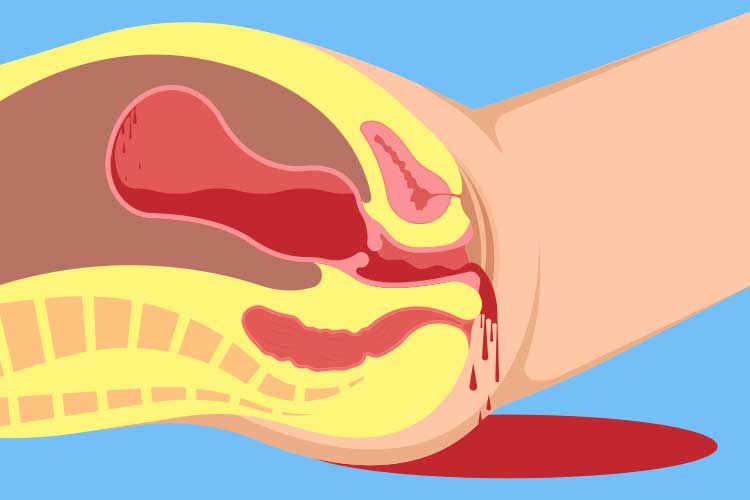
Postpartum hemorrhage is excessive bleeding following childbirth, defined as blood loss of 500 mL or more after vaginal delivery or 1000 mL or more after cesarean section, or any bleeding causing hemodynamic instability.
Uterine atony is the most common cause, where the uterus fails to contract adequately after delivery.
The causes are summarized as the 4 Ts: Tone (uterine atony), Trauma (genital tract injuries), Tissue (retained placental tissue), and Thrombin (coagulation disorders).
Early signs include excessive vaginal bleeding, a soft or boggy uterus, tachycardia, hypotension, pallor, dizziness, and reduced urine output.
Postpartum hemorrhage is primarily a clinical diagnosis based on estimation of blood loss, uterine tone assessment, and maternal vital signs; treatment should not be delayed for investigations.
The first-line treatment is uterine massage combined with oxytocin administration and immediate resuscitative measures.
Tranexamic acid should be administered as early as possible and within 3 hours of onset of bleeding to reduce mortality.
Carboprost (15-methyl prostaglandin F2α) is contraindicated in women with asthma due to the risk of bronchospasm.
Secondary postpartum hemorrhage refers to abnormal bleeding occurring from 24 hours up to 6 weeks after delivery, commonly due to retained products of conception or infection.
Hysterectomy is indicated when bleeding is life-threatening and unresponsive to medical and conservative surgical measures, particularly when fertility preservation is not required.
MCQ Test - Postpartum Hemorrhage Causes Diagnosis and Management
No MCQs available for this article.