Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Basic Life Support BLS Guidelines Stepwise CPR Airway Breathing Circulation Management
Frequently Asked Questions
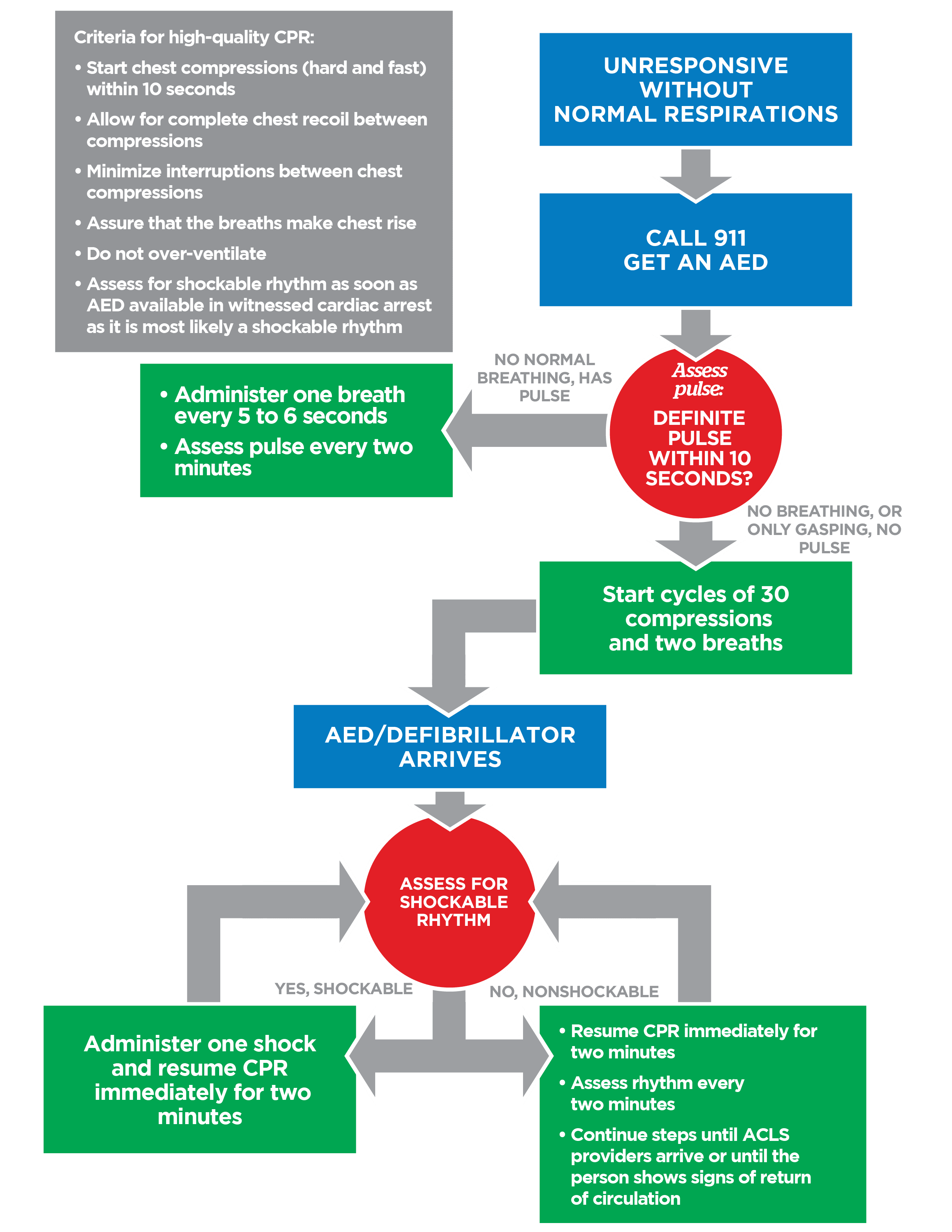
Basic Life Support is the immediate lifesaving care provided to patients with cardiac arrest respiratory arrest or airway obstruction focusing on airway breathing circulation and early defibrillation.
The goals of BLS are to maintain airway patency support breathing maintain circulation preserve brain function and prevent irreversible organ damage until advanced care is available.
High quality CPR includes compression rate of 100–120 per minute adequate depth full chest recoil minimal interruptions and avoidance of excessive ventilation.
CPR should be started immediately when an adult is unresponsive not breathing normally and has no palpable pulse.
The compression to ventilation ratio in adult BLS is 30 compressions followed by 2 breaths for both single and two rescuers.
Pediatric BLS uses a compression depth of one third of chest diameter and a ratio of 15:2 when two rescuers are present with greater emphasis on ventilation due to hypoxic causes.
The brachial pulse should be checked in infants during BLS.
An AED should be used as soon as it becomes available in any unresponsive patient with no normal breathing and no pulse.
CPR should be resumed immediately after the shock without checking the pulse or rhythm.
Severe choking in a conscious adult is managed with abdominal thrusts until the obstruction is relieved or the person becomes unresponsive.
CPR should be started and the mouth checked for visible foreign bodies before giving rescue breaths without performing blind finger sweeps.
Rescue breathing is ventilation without chest compressions indicated when a patient has a pulse but is not breathing.
Adults should receive one breath every 5 to 6 seconds which equals 10 to 12 breaths per minute.
In drowning victims rescue breaths are prioritized early as hypoxia is the primary cause of arrest.
Yes CPR should be continued until the patient is adequately rewarmed unless injuries are incompatible with life.
Common complications include rib fractures sternal fractures gastric distension and aspiration but these are acceptable compared to the benefit of survival.
BLS should be stopped when the patient shows signs of life advanced care takes over the rescuer is exhausted the scene becomes unsafe or a valid DNR order is present.
Early defibrillation rapidly terminates lethal arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation and significantly improves survival rates.
The chain of survival includes early recognition early CPR early defibrillation advanced life support and post cardiac arrest care.
Interruptions reduce coronary and cerebral perfusion pressure leading to poorer resuscitation outcomes.