Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
First Heart Sound S1 S3 S4 Atrial Myxoma Papillary Fibroelastoma Tuberculous Pericarditis Constrictive Pericarditis Complete Guide
Frequently Asked Questions
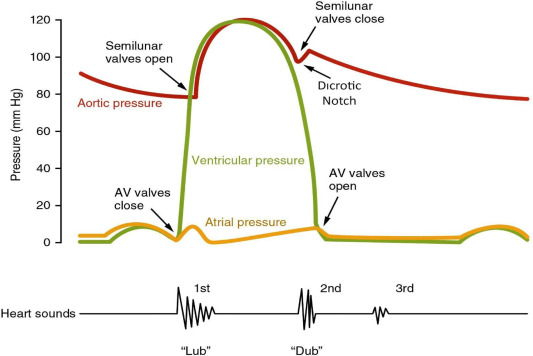
The first heart sound S1 is produced by closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves at the onset of ventricular systole. It marks the beginning of systole and is best heard at the apex.
Variation in S1 intensity depends on valve mobility, PR interval duration, ventricular contractility, and rhythm irregularity such as atrial fibrillation.
S3 indicates rapid ventricular filling and is physiological in children and young adults but pathological in older adults, commonly suggesting heart failure or volume overload.
S4 is caused by atrial contraction against a stiff, non-compliant ventricle, hence termed an atrial gallop and is associated with diastolic dysfunction.
S4 is absent in atrial fibrillation because it requires effective atrial contraction.
Atrial myxoma is the most common primary benign cardiac tumor, usually arising from the left atrium near the interatrial septum.
The classical triad includes obstructive symptoms, embolic events, and constitutional symptoms such as fever and weight loss due to IL-6 secretion.
A tumor plop is an early diastolic sound caused by sudden movement of an atrial myxoma through the mitral valve.
Papillary fibroelastoma is a benign cardiac tumor commonly arising from heart valves and is highly emboligenic despite its small size.
Transesophageal echocardiography is the investigation of choice due to its high sensitivity for small valvular lesions.
Tuberculous pericarditis is an infection of the pericardium caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, common in TB-endemic regions.
The stages include dry fibrinous, effusive, absorptive, and constrictive stages.
Corticosteroids reduce inflammation and decrease the risk of progression to constrictive pericarditis when used along with anti-tubercular therapy.
Constrictive pericarditis is a condition where the pericardium becomes thickened and fibrotic, restricting diastolic filling of the heart.
Tuberculous pericarditis is the most common cause of constrictive pericarditis worldwide.
A pericardial knock is an early diastolic sound caused by abrupt cessation of ventricular filling in constrictive pericarditis.
Constrictive pericarditis is differentiated by presence of pericardial thickening, pericardial knock, and ventricular interdependence on imaging and hemodynamic studies.
The definitive treatment is surgical pericardiectomy.
Presence of S3 in heart failure indicates elevated filling pressures and is associated with poor prognosis.
S4 heart sound best indicates diastolic dysfunction due to reduced ventricular compliance.
MCQ Test - First Heart Sound S1 S3 S4 Atrial Myxoma Papillary Fibroelastoma Tuberculous Pericarditis Constrictive Pericarditis Complete Guide
No MCQs available for this article.