Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Types Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment
Frequently Asked Questions
Multiple endocrine neoplasia is a group of inherited disorders characterized by the development of tumors in two or more endocrine glands, most commonly involving the parathyroid, pancreas, pituitary, thyroid and adrenal glands.
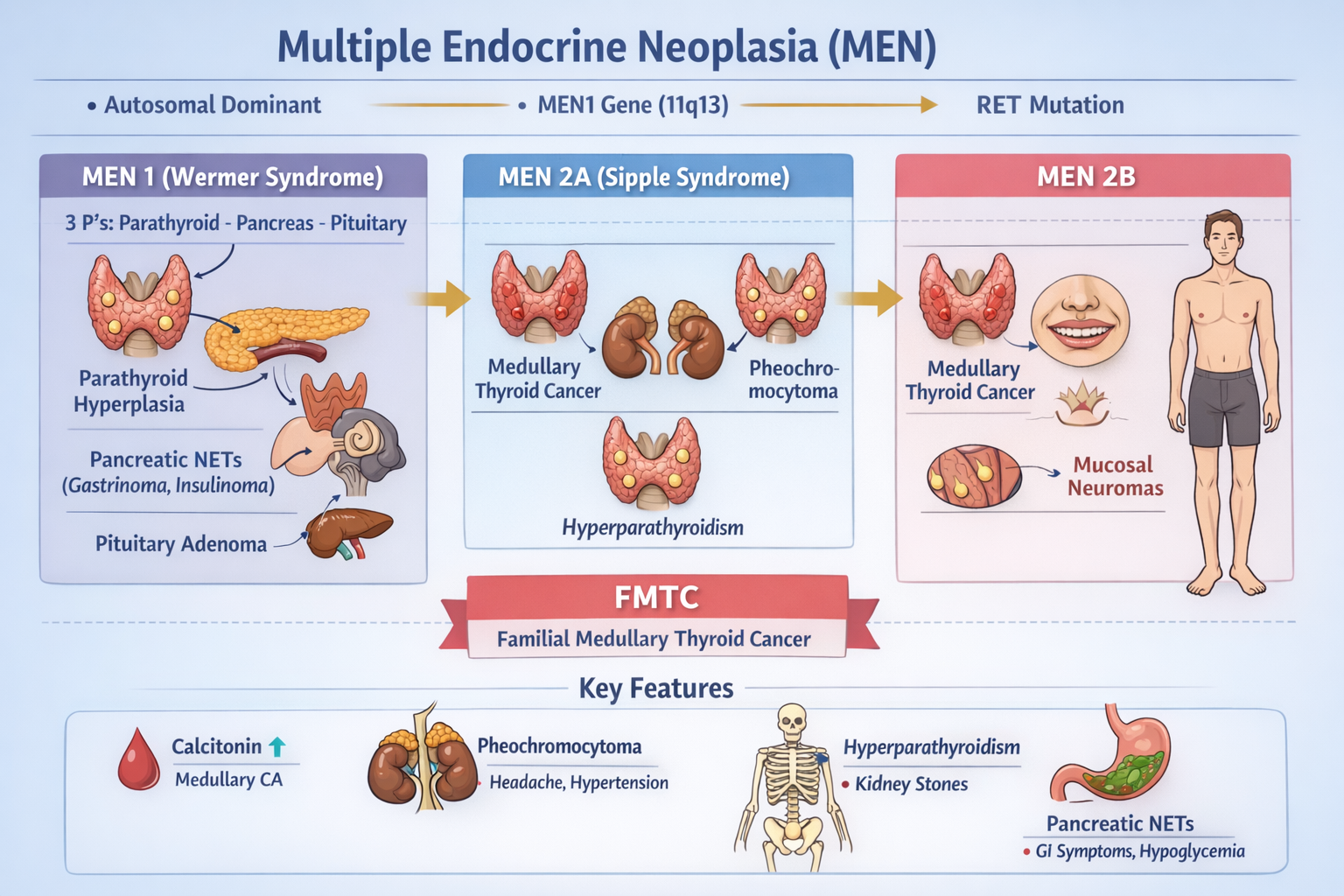
The main types are MEN 1, MEN 2A, MEN 2B and Familial Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma. Each type involves a different combination of endocrine tumors.
MEN is caused by inherited genetic mutations. MEN 1 is caused by mutation in the MEN1 gene, while MEN 2 syndromes are caused by mutations in the RET proto-oncogene.
MEN 1 causes tumors of the parathyroid glands, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors such as gastrinoma and insulinoma, and pituitary adenomas, most commonly prolactinomas.
Primary hyperparathyroidism due to parathyroid hyperplasia is the most common manifestation of MEN 1.
MEN 2A is characterized by medullary thyroid carcinoma, pheochromocytoma and primary hyperparathyroidism.
MEN 2B includes aggressive medullary thyroid carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, mucosal neuromas and a marfanoid body habitus.
Calcitonin is secreted by medullary thyroid carcinoma and is used as a tumor marker for diagnosis and monitoring in MEN 2.
Genetic testing identifies MEN1 or RET mutations and allows early diagnosis, family screening and preventive treatment such as prophylactic thyroidectomy.
Pheochromocytoma must be removed first because uncontrolled catecholamine release during thyroid surgery can cause fatal hypertensive crisis.
Zollinger Ellison syndrome is caused by gastrin-secreting tumors in MEN 1 leading to severe peptic ulcer disease and chronic diarrhea.
Prophylactic thyroidectomy is the preventive removal of the thyroid gland in RET mutation carriers to stop development of medullary thyroid carcinoma.
MEN cannot be cured genetically, but early detection and timely surgery and medical treatment can prevent complications and allow long-term survival.
Yes, MEN is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning a child has a 50 percent chance of inheriting the condition if one parent is affected.
Serum calcitonin and RET genetic testing are the most important screening tools for MEN 2.