Medical Disclaimer: This is educational content only, not medical advice. Consult a licensed healthcare provider for diagnosis/treatment. Information based on sources like WHO/CDC guidelines (last reviewed: 2026-02-13).
This article is being expanded for more depth. Check back soon!
Flexor Retinaculum Anatomy Structure Attachments Functions and Clinical Importance
Frequently Asked Questions
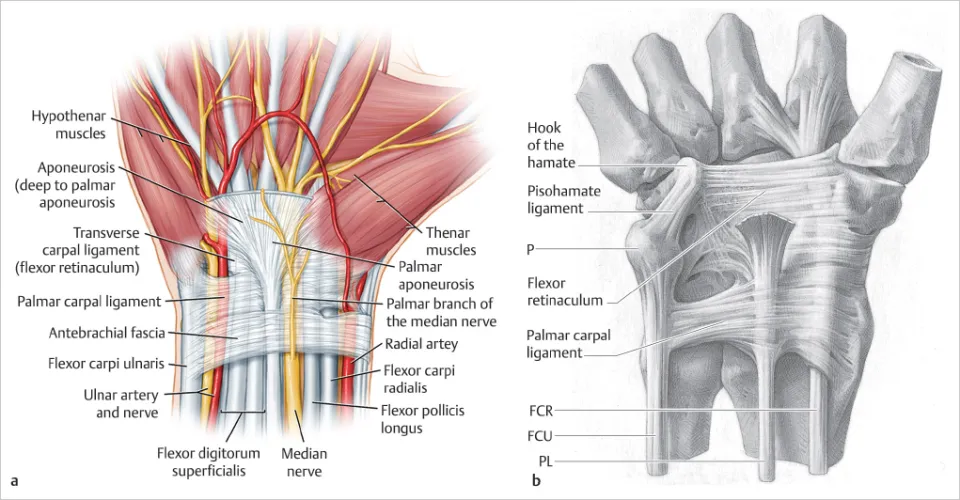
The flexor retinaculum is a strong fibrous band on the palmar aspect of the wrist that converts the carpal groove into the carpal tunnel and holds flexor tendons and the median nerve in place.
It is located on the anterior (palmar) surface of the wrist, stretching between the carpal bones on the radial and ulnar sides.
Laterally it attaches to the tubercle of scaphoid and crest of trapezium, and medially to the pisiform and hook of hamate.
The median nerve and nine flexor tendons (four flexor digitorum superficialis, four flexor digitorum profundus, and one flexor pollicis longus) pass deep to it.
The ulnar nerve, ulnar artery, and palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum.
Its main function is to prevent bowstringing of flexor tendons during wrist and finger flexion and to maintain mechanical efficiency.
Thickening or increased pressure beneath the flexor retinaculum compresses the median nerve, leading to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Because the palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve passes superficial to the flexor retinaculum and is not compressed.
No, the ulnar nerve passes superficial to the flexor retinaculum through Guyon’s canal.
The retinaculum is cut to increase the volume of the carpal tunnel and relieve pressure on the median nerve.
MCQ Test - Flexor Retinaculum Anatomy Structure Attachments Functions and Clinical Importance
No MCQs available for this article.